Introduction to Social Learning Theory in Social Work

Social work focuses on helping people improve their lives. Social Learning Theory is very useful for social workers because it explains how people develop behaviors through observation and interaction.
What Is Social Learning Theory?
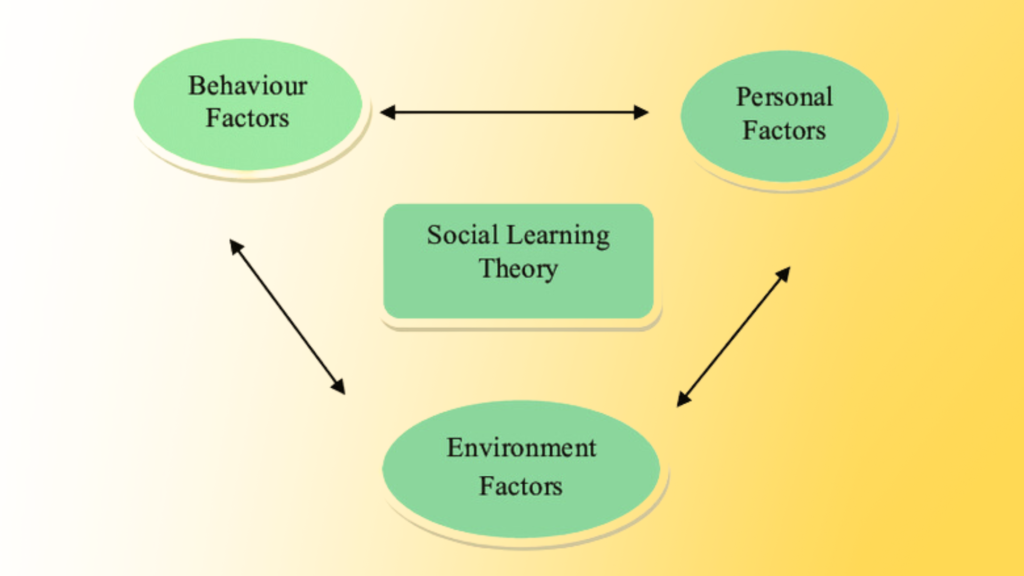
Social Learning Theory is a psychological theory that explains how people learn from their surroundings. It is especially important in social work because it helps professionals understand why people behave in certain ways and how they can encourage positive change.
What is the main idea of social learning theory?
The main idea of Social Learning Theory is that people learn by observing others. Instead of only learning through personal experience, they watch and imitate behaviors, especially from role models like parents, teachers, or friends. This learning process is influenced by rewards, punishments, and motivation. Social Learning Theory helps explain how people develop new skills, habits, and social behaviors in everyday life
History of Social Learning Theory
Albert Bandura introduced Social Learning Theory in the 1960s. He believed that people learn not only from personal experience but also by watching others. His famous “Bobo doll experiment” showed that children who watched an adult behaving aggressively toward a toy were more likely to act aggressively themselves.
Assumptions of Social Learning Theory
Social Learning Theory is based on a few key assumptions:
- People learn by observing others.
- Learning is influenced by rewards and punishments.
- Learning involves mental processes like thinking and motivation.
- People can control their own behavior by choosing what they learn and imitate.
Social Learning Theory Examples
- A child learns to say “thank you” by watching their parents.
- A student learns to be kind by observing a kind teacher.
- A person learns healthy habits by watching fitness influencers online.
Basic Principles of Social Learning Theory
Social Learning Theory is built on a few key ideas:
- Observation: People learn by watching others.
- Imitation: People copy behaviors they see.
- Reinforcement: Rewards and punishments shape learning.
- Mental Processes: Thinking and motivation play a big role in learning.
Recap
In simple terms, Social Learning Theory says that learning happens in a social setting. Instead of learning only from books, we also learn from people around us!
Applications of Social Learning Theory
Social workers use Social Learning Theory in many ways. They help people learn positive behaviors by showing them role models, offering encouragement, and creating supportive environments.
How Does Social Learning Theory Apply to Social Work?
- Helping children and families: Social workers teach parents how to be positive role models.
- Behavioral therapy: They help people change negative habits by replacing them with positive behaviors.
- Community programs: They create support groups where people can learn from each other.
Core Concepts of Social Learning Theory

People Can Learn Through Observation
Have you ever watched a friend play a new video game and then tried it yourself? That’s observational learning! We learn by watching what others do and seeing the results of their actions.
Mental States Are Important to Learning
Learning is not just about copying others; it also depends on motivation and thoughts. If someone believes they can succeed, they are more likely to try and keep going even when things get difficult.
Learning Does Not Necessarily Lead to Change
Just because someone learns something does not mean they will use it. For example, you may learn about healthy eating, but you might still prefer eating fast food. Learning happens, but action depends on motivation and choice.
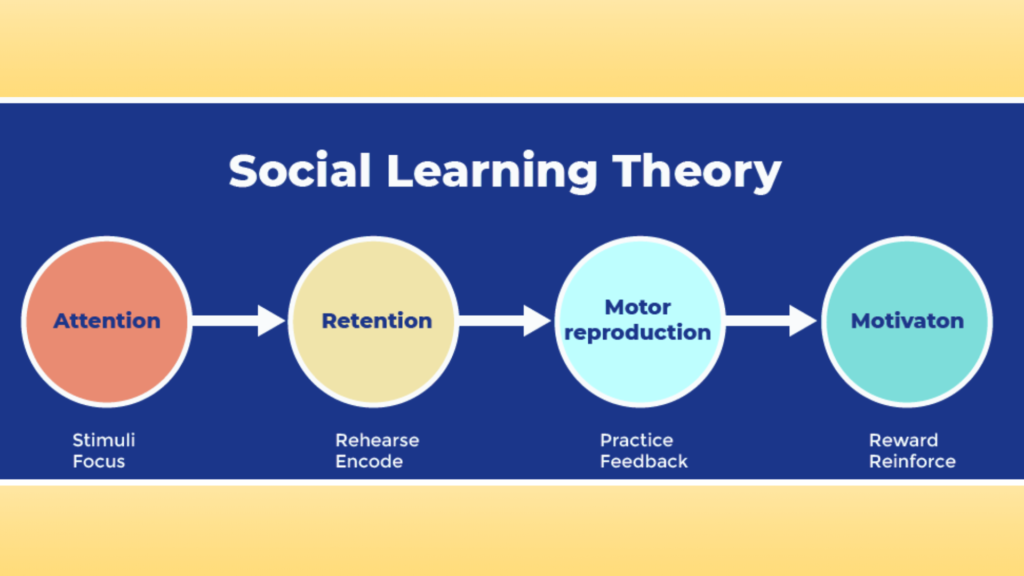
Key Factors for Social Learning Success
For social learning to work well, these factors are important:
- Attention: Paying close attention to what others do.
- Retention: Remembering what was learned.
- Reproduction: Being able to do what was learned.
- Motivation: Wanting to apply what was learned.
Real-World Applications for Social Learning Theory
Social Learning Theory is everywhere! It helps in schools, workplaces, and even in families. Teachers use it to show good behavior, parents use it to teach kids manners, and companies use it for employee training.
Strengths and Criticisms of Social Learning Theory
Strengths:
- Explains how learning happens in real life.
- Shows the power of role models.
- Useful in education and social work.
Criticisms:
- Doesn’t explain all types of learning.
- Some behaviors may be influenced by biology, not just observation.
Also Read it: Important Theories and Practice Models Used in Social Work
Social Learning Theory Books and Resources
Books on Social Learning Theory
- “Self-Efficacy: The Exercise of Control” – Written by Albert Bandura, this book explores the concept of self-efficacy, explaining how believing in one’s abilities leads to a more successful and fulfilling life.
- “Self-Efficacy in Changing Societies” – Edited by Albert Bandura, this book examines how personal beliefs interact with cultural influences to shape human behavior and life outcomes. Topics include personal agency, competency development, and family influence.
- “Social Learning Theory” – A foundational book by Albert Bandura that delves into how people learn through observation, imitation, and cognitive processes. It highlights the importance of role models and self-regulation in shaping behavior.
- “Theories for Direct Social Work Practice” by Joseph Walsh – This book introduces eleven essential theories used in social work practice, explaining their role in assessing and helping individuals, families, and groups.
- “Case Studies in Social Work Practice” edited by Craig W. LeCroy – This book presents real-world case studies that demonstrate how social learning principles are applied in social work, making theoretical concepts more relatable and practical.
- “Social Learning and Social Structure: A General Theory of Crime and Deviance” by Ronald Akers – This book examines the role of social learning in shaping criminal behavior, discussing how environmental and social influences contribute to deviance.

Online Resources on Social Learning Theory
- Bobo Doll Experiment – This article by Saul McLeod explains the famous Bobo Doll experiments conducted by Albert Bandura. It details the experiments’ methodology, results, and impact on social learning theory.
- ScienceDirect.com – This website provides access to academic articles and book chapters on social learning theory, covering topics like peer influence, social anxiety, child development, and aggression.
- “5 Social Work Theories That Inform Practice” by Social Work Helper – This resource simplifies five key social work theories, including social learning theory, explaining their real-world applications in a clear and concise manner.
These books and resources offer valuable insights into social learning theory, helping readers understand how human behavior is shaped by observation, imitation, and social






2 Comments